Abstract
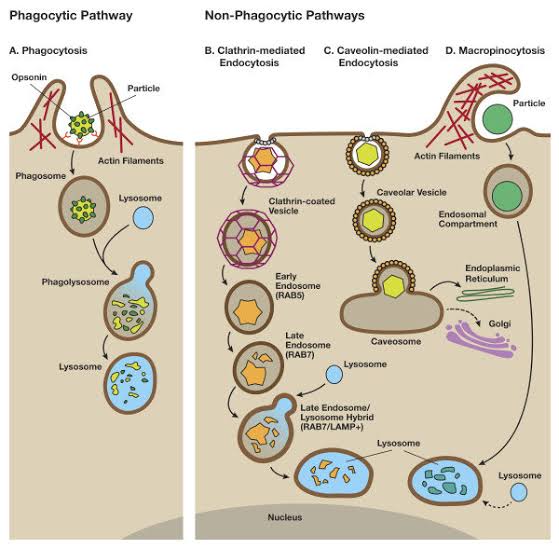
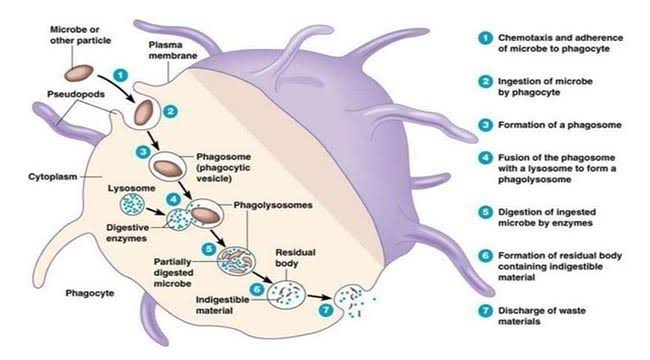
Phagocytosis of pathogens by macrophages starts the natural insusceptible reaction, which thus coordinates the versatile reaction. So as to separate between irresistible specialists and self, macrophages have developed a confined number of phagocytic receptors, similar to the mannose receptor, that perceive preserved themes on pathogens. Pathogens are likewise phagocytosed by supplement receptors after generally vague opsonization with supplement and by Fc receptors after explicit opsonization with antibodies. Every one of these receptors instigate modifications in the actin cytoskeleton that lead to the disguise of the molecule. In any case, significant contrasts in the atomic components hidden phagocytosis by various receptors are presently being valued. These remember contrasts for the cytoskeletal components that intervene ingestion, contrasts in vacuole development, and contrasts in incendiary reactions. Irresistible operators, for example, M. tuberculosis, Legionella pneumophila, and Salmonella typhimurium, enter macrophages by means of heterogeneous pathways and adjust vacuolar development in a way that favours their endurance. Macrophages additionally assume a significant job in the acknowledgment and freedom of apoptotic cells; a striking element of this procedure is the nonappearance of a provocative reaction.