Various innovative vaccines are additionally being developed and being used.
DNA VACCINE:
Another investigational way to deal with immunization includes introducing hereditary material or genetic materials encoding the antigen or antigens against which an immune reaction is looked for. The body’s own cells at that point utilize this hereditary material to create the antigens. Expected points of interest of this methodology incorporate the incitement of expansive long terms immune responses, magnificent vaccine steadiness and relative simplicity of enormous scope vaccine manufacture.
DNA plasmid vaccines include a little round bit of DNA considered a plasmid that conveys qualities or genes encoding proteins from the microbe of interest. The assembling cycle for DNA plasmid vaccines is settled, permitting test vaccines to be immediately evolved to address rising or reappearing irresistible illnesses. NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center has created DNA vaccines to address a few viral ailment dangers during several outbreaks, including SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in 2003, H5N1 avian flu in 2005, H1N1 pandemic flu in 2009, and Zika virus in 2016.
A DNA vaccine utilizes duplicates of few HIV genes, which are embedded into bits of DNA called plasmids. The HIV qualities will create proteins fundamentally the same as the ones found in genuine HIV. After vaccination, the body’s immune framework may react to the HIV-like proteins, and battle the genuine virus if the inoculated individual is later presented to it.
When the genetic materials from a microorganism have been investigated, researchers could endeavor to make a DNA vaccine against it.
DNA vaccines comprise of plasmid DNA encoding antigenic proteins which are infused straightforwardly into the muscle of the recipient. The DNA itself embeds into the person’s cells, which at that point produce the antigen from the infectious agent. DNA vaccines have preferences over many existing vaccines. For instance, the encoded protein is a local type of the host and has no denaturation or adjustment. Along this, the immune response is indistinguishable from the antigen communicated by the microbe.
RNA VACCINE:
Vaccines dependent on messenger RNA (mRNA), a mediator among DNA and protein, additionally are being created. Latest technological advances, to a great extent conquered issues with the instability of mRNA and the trouble of conveying it into cells, and some mRNA vaccines have shown empowering early outcomes. For instance, NIAID-upheld specialists built up a test mRNA vaccine that secured mice and monkeys against Zika virus disease after a single portion of dose.
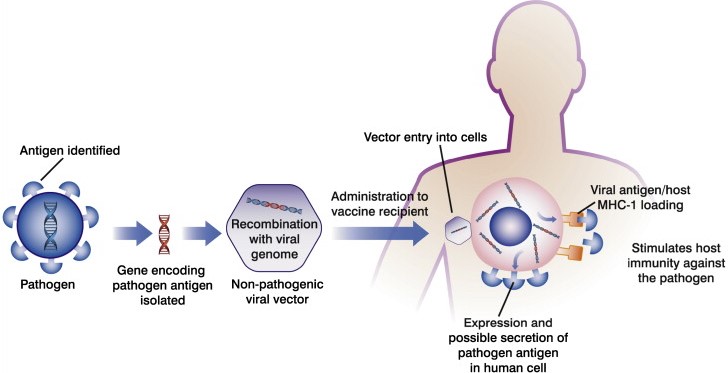
RECOMBINANT VACCINES:
As opposed to conveying DNA or mRNA straightforwardly to cells, a few vaccines utilize an innocuous virus or bacterium as a vector, or transporter, to bring hereditary (genetic) material into cells. A few such recombinant vector vaccines are endorsed to shield animals from irresistible maladies, including rabies and distemper (viral illness of domestic canines, dogs and different animals). A large number of these veterinary vaccines depend on an innovation created by NIAID scientists that utilizes debilitated or weakened variants of a poxvirus to convey the microbe’s genetic material. Now, NIAID-upheld researchers are creating and assessing recombinant vector vaccines to shield people from viruses, for example, HIV, Zika virus and Ebola virus, etc..
Recombinant vector vaccines are experimental vaccines like DNA vaccines, however they utilize a constricted or attenuated virus or bacterium to acquaint microbial DNA with cells of the body. “Vector” alludes to the virus or bacterium utilized as the transporter or carrier.
In nature, viruses lock on to cells and infuse their hereditary material into them. In the lab, a comparable cycle can be led utilizing certain innocuous or weakened viruses and insert parts of the hereditary material from different organisms into them. The transporter or carrier viruses then ship that microbial DNA to cells. Recombinant vector vaccines closely similar to a natural ailments or infections and in this way work superbly for stimulating the immune framework. Researcher are dealing with both bacterial and viral-based recombinant vector vaccines for TB, HIV, rabies, and measles.
The quality fragment or genetic segment for a protein from the illness causing microbe that is known to invigorate a defensive immune response (protein of interest) is embedded into the genetic material of another cell, for example, a yeast cell. At the point when the cell recreates it has a similar shape as the protein of intrigue. Yeats cells are utilized for the hepatitis B and human papillomavirus.
Recombinant vaccines are made utilizing bacterial or yeast cells to make the vaccine. A little bit of DNA is taken from the virus or bacterium against which we need to ensure protection. This is embedded into different cells to make them produce enormous amounts of dynamic element for the vaccine (normally only a single protein or sugar molecules). For instance, to make the hepatitis B vaccine, part of the DNA from the hepatitis B virus is embedded into the DNA of yeast cells. These yeast cells are then ready to deliver one of the surface proteins of the hepatitis B virus, and this is processed and purified and utilized as the dynamic ingredient in the vaccine.



A large number of these veterinary vaccines depend on an innovation created by NIAID scientists that utilizes debilitated or weakened variants of a poxvirus to convey the microbe’s genetic material… Good work.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Glad …that you read in so detail..😅
LikeLike